
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |



























| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |


























Grumman F7F-3 Tigercat
USN Twin-engine Single-Seat Carrier-Borne Fighter, USA
Archive Photos
Grumman F7F-3 Tigercat-King of the Cats (N207F, BuNo 80412) 1999 Palm Springs Air Museum, Palm Springs, California (Photos by John Shupek) (Photos by John Shupek)


Grumman F7F Tigercat Overview [1]
The Grumman F7F Tigercat is a heavy fighter aircraft that served with the United States Navy (USN) and United States Marine Corps (USMC) from late in World War II until 1954. It was the first Twin-engine fighter to be deployed by the USN. While the Tigercat was delivered too late to see combat in World War II, it saw action as a night fighter and attack aircraft during the Korean War.
Designed initially for service on Midway-class aircraft carriers, early production F7Fs were land-based variants. The type was too large to operate from older and smaller carriers, and only a late variant (F7F-4N) was certified for carrier service.
Design and Development [1]
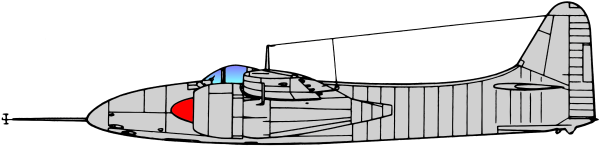
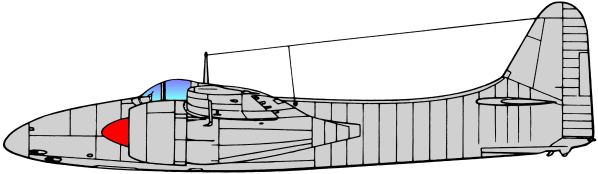
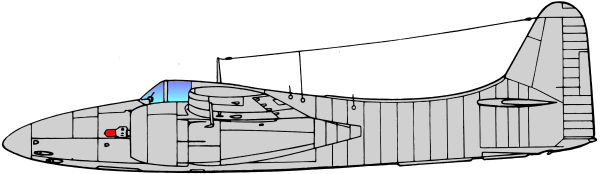
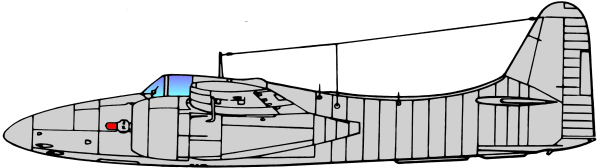
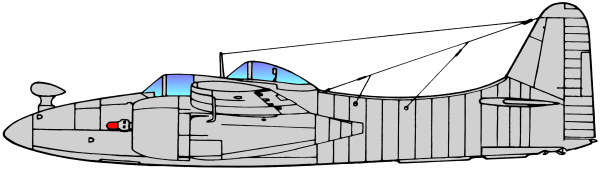
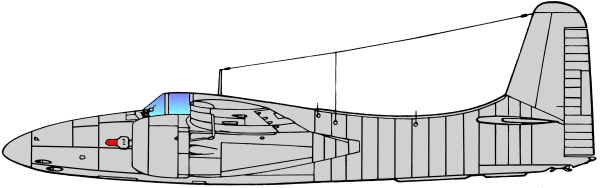
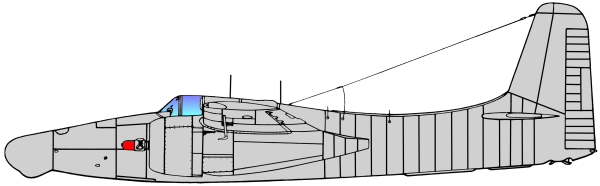

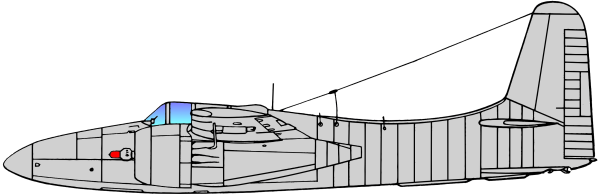
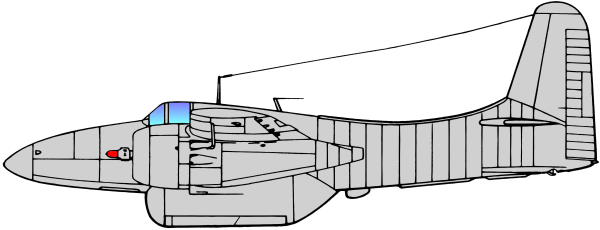
Based on the earlier Grumman XP-50 that was eventually canceled, the company developed the XP-65 (Model 51) further for a future convoy fighter concept. In 1943, work on the XP-65 was terminated in favor of the design that would eventually become the F7F. The contract for the prototype XF7F-1 was signed on 30 June 1941. Grumman’s aim was to produce a fighter that outperformed and outgunned all existing fighter aircraft, and that had an auxiliary ground attack capability.
Performance of the prototype and initial production aircraft met expectations; the F7F was one of the fastest piston-engine fighters, with a top speed significantly greater than single-engine USN aircraft - 71 mph faster than a Grumman F6F Hellcat at sea level.[3] Captain Fred Trapnell, one of the premier USN test pilots of the era, stated: It’s the best damn fighter I’ve ever flown. The F7F was to be heavily-armed: four 20mm cannon and four 50 caliber (0.50 in; 12.7 mm) machine guns, as well as underwing and under-fuselage hardpoints for bombs and torpedoes. This speed and firepower was bought at the cost of heavy weight and a high landing speed, but what caused the aircraft to fail carrier suitability trials was poor directional stability with only one engine operational, as well as problems with the tailhook design. The initial production series was, therefore, used only from land bases by the USMC, as night fighters with APS-6 radar.
While the F7F was initially also known as the Grumman Tomcat7rdquo;, this name was abandoned, because it was considered at the time to have excessively sexual overtones; (from the 1970s, the name Tomcat became commonly associated with, and officially used by the Navy for, another Grumman design, the F-14 twin-jet carrier-based interceptor. The first production variant was the single-seat F7F-1N aircraft; after the 34th production aircraft, a second seat for a radar operator was added and these aircraft were designated F7F-2N.
A second production version, the F7F-3, was modified to correct the issues that caused the aircraft to fail carrier acceptance, and this version was again trialled on the USS Shangri-La. A wing failure on a heavy landing caused the failure of this carrier qualification as well. F7F-3 aircraft were produced in day fighter, night fighter, and photo-reconnaissance versions.
The final production version, the F7F-4N, was extensively rebuilt for additional strength and stability, and did pass carrier qualification, but only 12 were built.
Operational History [1]
Marine Corps night fighter squadron VMF(N)-513 flying F7F-3N Tigercats saw action in the early stages of the Korean War, flying night interdiction and fighter missions and shooting down two Polikarpov Po-2 biplanes. This was the only combat use of the aircraft.
Most F7F-2Ns were modified to control drones for combat training, and these gained bubble canopies over the rear cockpit for the drone controller. An F7F-2D used for pilot transitioning also had a rear sliding, bubble canopy.
In 1945, two Tigercats, serial numbers TT346 and TT349, were evaluated, but rejected by the British Royal Navy, who preferred a naval version of the de Havilland Hornet.
Variants [1]
Grumman F7F Tigercat Specifications [2]
| Variant ➔ | F7F-1 | F7F-2N | F7F-3 | F7F-3N |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIMENSIONS | ||||
| Wing span | 51 ft 6 in (15.70 m) | 51 ft 6 in (15.70 m) | 51 ft 6 in (15.70 m) | 51 ft 6 in (15.70 m) |
| Wing span (folded) | 32 ft 2 in (9.80 m) | 32 ft 2 in (9.80 m) | 32 ft 2 in (9.80 m) | 32 ft 2 in (9.80 m) |
| Length | 45 ft 4.5 in (13.83 m) | 45 ft 4.5 in (13.83 m) | 45 ft 4.5 in (13.83 m) | 46 ft 9.25 in (14.26 m) |
| Height | 15 ft 2 in (4.62 m) | 15 ft 2 in (4.62 m) | 16 ft 4 in (4.98 m) | 16 ft 4 in (4.98 m) |
| Wing area | 455 ft² (42.27 m²) | 455 ft² (42.27 m²) | 455 ft² (42.27 m²) | 455 ft² (42.27 m²) |
| WEIGHTS | ||||
| Empty | 15,943 lb (7,232 kg) | 16,321 lb (7,403 kg) | 16,270 lb (7,380 kg) | 16,954 lb (7,690 kg) |
| Loaded | 21,425 lb (9,718 kg) | 21,857 lb (9,914 kg) | 21,720 lb (9,852 kg) | 21,960 lbs (9,961 kg) |
| Maximum | 22,560 lb (10,233 kg) | 26,194 lb (11,881 kg) | 25,720 lb (11,666 kg) | 26,167 lb (11,869 kg) |
| Wing loading* | 47.1 lb/ft² (299.9 kg/m²) | 48.1 lb/ft² (234.5 kg/m²) | 47.7 lb/ft² (233.1 kg/m²) | 48.3 lb/ft² (235.7 kg/m²) |
| Power loading* | 5.1 lb/hp (2.3 kg/hp) | 5.2 lb/hp (2.4 kg/hp) | 5.2 lb/hp (2.4 kg/hp) | 5.2 lb/hp (2.4 kg/hp) |
| * Wing and power loadings are calculated at normal loaded weight and maximum takeoff power. | ||||
| PERFORMANCE | ||||
| Maximum speed | 445 mph @ 16,000 ft (716 kmh @ 4,875 m) | 431 mph @ 20,600 ft (693 kmh @ 6,280 m) | 450 mph @ 21,500 ft (724 kmh @t 6,555 m) | 436 mph @ 24,500 ft (702 kmh @ 7,470 m) |
| Cruising speed | 177 mph (285 kmh) | 183 mph (294 kmh) | 222 mph (357 kmh) | 235 mph (378 kmh) |
| Climb rate | 4,360 ft/min (22 m/sec) | 4,540 ft/min (23 m/sec) | 6,040 ft/min (31 m/sec) | 4,100 ft/min (21 m/sec) |
| Service ceiling | 36,200 ft (11,035 m) | 39,800 ft (12,130 m) | 40,700 ft (12,405 m) | 37,600 ft (11,460 m) |
| Normal range | 1,170 miles (1,885 km) | 960 miles (1,545 km) | 1,200 miles (1,930 km) | 810 miles (1,305 km) |
| Maximum range | 1,485 miles (2,390 km) | 1,250 miles (2,010 km) | 1,900 miles (3,055 km | 1,360 miles (2,190 km |
| ASSIGNED BuNos | ||||
| XF7F-1 | 03549/03550 | |||
| F7F-1 | 80259/80260 and 80262/80293 | |||
| XF7F-2 | 80261 | |||
| F7F-2N | 80294/80358 | |||
| F7F-3/F7F-3N/F7F-3P | 80359/80608 | |||
| XF7F-4N | 80548 | |||
| F7F-4N | 80609/80620 | |||
References